- AlQuds
- Gaza
- Nablus
- Ramallah
- Haifa
- Al-Khalil
- Bethlehem
- Ginin
- Jericho
- Tulkarm
- Rafah
- Khan Yunis
AlQuds
AlQuds The City of Peace, the place of the Prophet Muhammad's Night Journey, and the flower of all cities. It is the
Palestinian city of Al-Quds, considered one of the holiest and oldest cities in the world.
The city of Al-Quds is distinguished as the place associated with the most prominent religious events and figures in
the world. It is home to three of the most important sacred sites in the major monotheistic religions:
- Al-Aqsa mosques
- The Church of the Holy Sepulchre
- The Western Wall (also known as the Wailing Wall)
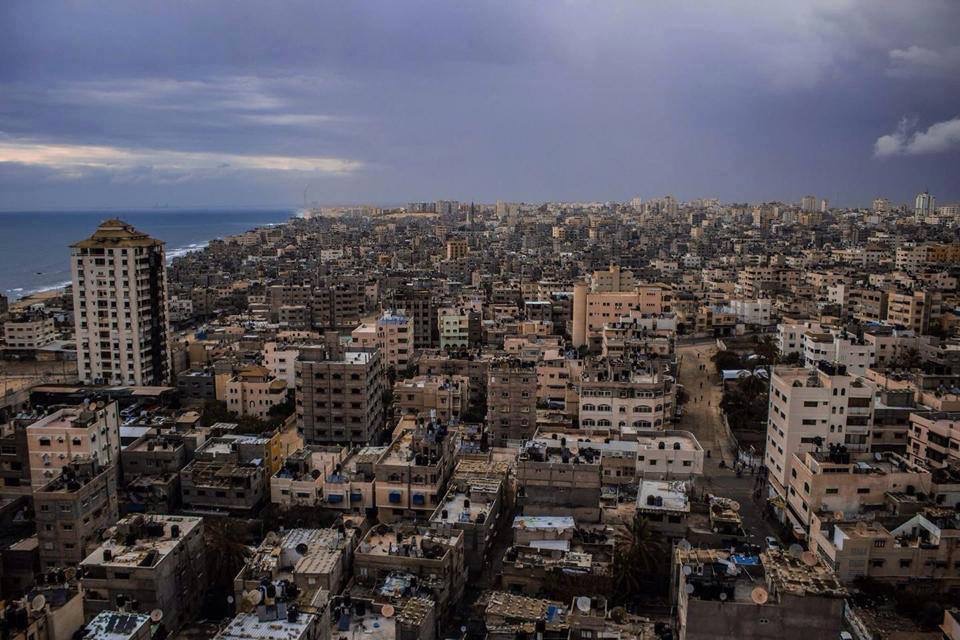
Gaza
Gaza's roots dig deep into antiquity, with evidence of settlement dating back to the Bronze Age. Throughout the ages, it
has been a strategic trading post, connecting continents and cultures. Pharaohs, Persians, Greeks, Romans, and Crusaders
have all left their mark on its storied streets.
The Modern Epoch:
In the 20th century, Gaza witnessed seismic shifts. From Ottoman rule to British mandate, and eventually, the Israeli
occupation following the Arab-Israeli War of 1948, Gaza became a focal point of regional conflict. The 1967 Six-Day War
brought Gaza under Israeli control, marking the beginning of a protracted struggle for self-determination.
A Symbol of Struggle:
Gaza City became synonymous with resistance and resilience. Waves of Palestinian refugees, displaced from their homes
during the creation of Israel, found sanctuary within its borders. Decades of occupation, conflict, and blockade have
taken their toll on Gaza's infrastructure and economy, yet its people endure, steadfast in their pursuit of justice and
freedom.
The Siege and Its Toll:
In recent years, Gaza has been besieged by a blockade, severely restricting the flow of goods and people in and out of
the territory. This blockade, coupled with periodic military incursions and conflicts, has led to dire humanitarian
conditions, with shortages of essential resources like water, electricity, and medical supplies.
The Spirit of Resilience:
Despite the challenges, Gaza City pulsates with life. Its bustling markets, vibrant culture, and indomitable spirit defy
the odds. From fishermen braving the blockade to artisans preserving traditional crafts, Gaza's resilience is a
testament to the human spirit's capacity to endure and thrive amidst adversity.
A Call for Hope:
As the world bears witness to Gaza's plight, calls for justice and peace reverberate across the globe. The people of
Gaza yearn for a future free from occupation and blockade, where they can rebuild their lives and realize their
aspirations for prosperity and dignity.
In Conclusion:
Gaza City stands as a testament to the enduring human spirit in the face of adversity. Its history, marked by struggle
and resilience, serves as a reminder of the urgent need for a just and lasting resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian
conflict—one that respects the rights and dignity of all people involved.
As Gaza City continues to navigate the complexities of its past and present, one thing remains clear: its people are
determined to shape their own destiny and reclaim their place in the tapestry of human history.
Some Israeli massacres
Deir Yassin Massacre (1948)
Gaza Beach Bombing (2006)
Gaza Hospital Bombings (2023)
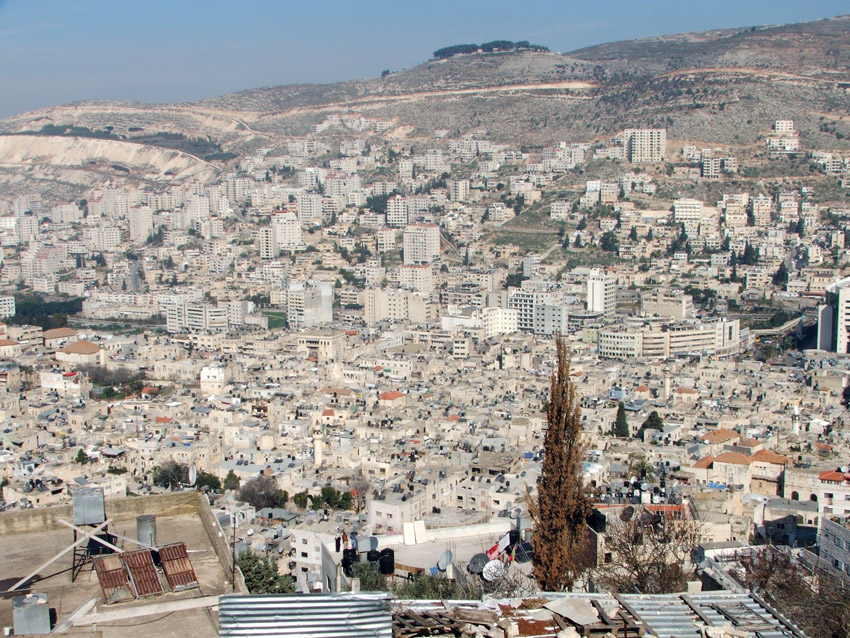
Nablus
Nablus is one of the oldest and most important cities in Palestine, located in the northern West Bank. The city is
renowned for its rich history and cultural landmarks.
History and Location
Founded by the Roman Emperor, Vespasian in 72 CE as Flavia Neapolis, the city has been ruled by many empires over
the
course of its almost 2,000-year-long history. In 636 CE, Neapolis, along with most of Palestine, came under the rule
of
the Islamic Arab Caliphate of (Omar Ibn Al-Khattab); where its name was changed to the Arabic name of Nablus.
In the heart of Nablus lies the old city consisting of eight major quarters: Yasmina, Qaryun, Aqaba, Qaysariyya,
Habala,
Faqous, Naser and Gharb. The old city is densely populated with 9000 inhabitants whereas Nablus district is
populated
with 389,328 inhabitants.
location wikipedia.
Main Landmarks
- The Old City:The old part of Nablus contains traditional markets, mosques, churches, and historical buildings,
making it a significant tourist destination.
- Nablus Mountains:Mount Gerizim and Mount Ebal offer stunning natural views and significant historical and
religious sites, including the Samaritan holy sites on Mount Gerizim.
- An-Najah National
University:One of the largest and oldest universities in Palestine, playing a crucial role in
higher education and research in the region.
Culture and Heritage
Nablus is known for its rich culture and diverse heritage, reflected in its traditional cuisine, folklore, and
cultural
festivals. Nablus sweets, such as the famous Nablus knafeh, are popular both inside and outside of Palestine.
Nablus combines ancient history with modern life, making it one of the vibrant and prominent cities in Palestine.
Ramallah
Ramallah is a major city in the central West Bank, serving as the de facto administrative capital of the Palestinian
Authority. It is known for its vibrant cultural scene, economic activity, and political significance wikipedia
History and Location
Ramallah is located about 10 kilometers north of Jerusalem. It was originally a Christian village but has grown
significantly over the years. The name "Ramallah" translates to "God's Hill" in Arabic. The city has a rich history,
with its origins dating back to the mid-16th century.
Main Landmarks
- Al-Manara Square: The central square of Ramallah, a bustling area surrounded by shops, restaurants, and important
buildings.
- Yasser Arafat Museum:Dedicated to the life and legacy of the late Palestinian leader, providing insights into
Palestinian history and politics.
- Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center:A prominent cultural institution that hosts art exhibitions, literary events, and
performances.
Cultural and Political Significance
Ramallah is considered the cultural capital of the West Bank, hosting numerous cultural festivals, music events, and
art
exhibitions. The city is also the political heart of the Palestinian Authority, housing government buildings and the
offices of the President and Prime Minister of Palestine.
Ramallah offers a blend of modernity and tradition, making it a central point for economic, cultural, and political
activities in the West Bank. Its dynamic atmosphere and strategic importance continue to shape its development and
influence within Palestine Some sources.
Haifa Haifa is an ancient Canaanite prehistoric city built on Mount Carmel.
Haifa is located on the Mediterranean coast in northern Palestine at the confluence of latitude 32.49 north and
longitude 35 east. It is the meeting point of the Mediterranean Sea with both the plain and Mount Carmel. This makes it
an obligatory crossing point, as the width of the coastal plain is less than 200 metres.
Its strategic location made it a seaport that became the first in Palestine. It also made it a gateway to Iraq, Jordan,
and South Syria across the Mediterranean.
It was of commercial and military importance throughout its history, which is why it was exposed to colonial ambitions,
starting from the Crusader invasion until the Zionist occupation.
Railway lines extended to it to connect it with Palestinian and Arab cities, from Gaza and Lod to Beirut, Tripoli and
Damascus.
As for its name, some believe that it came from the word Hafa, meaning beach, and it may be taken from Al-Haifa, meaning
a side. Others believe that the origin of Al-Haifa is an umbrella or a reserve, because Mount Carmel surrounds it,
protects it, and shades it.
It was mentioned in ancient books as Skymenos, and the Crusaders called it Kifa and sometimes Sykamenion, which in Greek
means mulberry tree. This may be due to the large number of mulberry trees in Haifa.
Haifa was conquered during the reign of the Umayyad Caliph Muawiyah bin Abi Sufyan, by Amr bin Al-Aas in 633 AD. As a
result, Arab tribes began to settle in Palestine, especially in the areas of the Palestinian coast, and Haifa remained
part of the Islamic state throughout the Umayyad and Abbasid eras.
Foreign settlement in the city began in 1868 by a group of German families coming from southwestern Germany. They
established a settlement in the western part of the city and followed the construction of German settlements in the
coastal area. These settlements eventually paved the way for the establishment of the first German neighborhood in the
modern style in The city, which is the "Carmelheim" neighborhood on Mount Carmel Sources.
It is noteworthy that the city was occupied by Jewish organizations on April 21, 1948, after several battles and
massacres carried out against the Arab residents of the city and its suburbs, which resulted in the mass expulsion of
most of these residents from their neighborhoods, and the direct replacement of the names of Arab streets and areas with
Hebrew After the Jews occupied the city, its Palestinian Arab residents were forced to leave, their homes were confiscated, and
they were not allowed to return to it. It was occupied by Jewish immigrants, who later increased, and their number has
now reached about 300,000 people.
Al-Khalil Al-Khalil is a Palestinian city, and the administrative center of Hebron Governorate. It is located in the West Bank, about 35 km south of Jerusalem. It was founded by the Canaanites in the Early Bronze Age, and today it is considered the largest city in the West Bank in terms of population and area, as its population in 2016 reached approximately 215 thousand people, and its area is 42 km2. The city is distinguished by its economic importance, as it is considered one of the largest economic centers in the West Bank. Hebron has religious importance for the three Abrahamic religions, as in the center of the city is the Ibrahimi Mosque, which contains the shrines of the prophets Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, and their wives. The city of Hebron is currently divided into the old and the new city, and is administered by the Hebron Municipality, which was established in 1927. It is also the center of the Hebron Governorate, whose current administrative division includes dozens of villages and towns, and the governorate’s population is estimated at more than 684 thousand people (2014). The old city is located adjacent to the Ibrahimi Mosque. It consists of old alleys, houses, and shops, and includes many markets. Israel closes large parts of it and deploys Israeli army forces there due to a recent gathering of Orthodox Jews seeking to control real estate in that area. Israel controls about 20% of the city's area according to the Hebron redeployment agreement in 1997, but the Palestinian Authority is responsible for managing the civil affairs of the Palestinians there. The city is also surrounded by many Israeli settlements, the largest of which is Kiryat Arba, and Jewish settlements and communities are governed by a separate municipal body. The city is one of the four holy cities in the Jewish religion. wikipedia
Bethlehem
Bethlehem, located in the central West Bank, Palestine, approximately 10 kilometers south of Jerusalem, is one of the
oldest cities in the world and holds immense historical and religious significance. Its history spans thousands of
years, encompassing various periods and cultural influences.
Ancient History
Birthplace of Jesus:
- According to the New Testament, Bethlehem is the birthplace of Jesus Christ. The Gospels of Matthew and Luke describe
Jesus' birth in Bethlehem, making the city a major Christian pilgrimage site.
- The Church of the Nativity, built over the site traditionally considered to be the birthplace of Jesus, was
commissioned by Constantine the Great in 327 CE and is one of the oldest continuously operating churches in the world.
rsians invaded in 614 CE, causing significant destruction, but the Church of the Nativity was spared.
Islamic Periods
Early Islamic Period:
- In 637 CE, Bethlehem came under Muslim control. The city remained a significant Christian pilgrimage site, and the
Muslim rulers generally protected the Christian holy places.
Modern History
British Mandate and Jordanian Rule:
- After World War I, Bethlehem became part of the British Mandate of Palestine.
- Following the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Bethlehem was annexed by Jordan.
Israeli Occupation:
- In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Bethlehem was occupied by Israel, leading to significant political and social
changes.
- The construction of the Israeli West Bank barrier in the early 21st century has had a profound impact on the city's
economy and mobility of its residents.
Contemporary Bethlehem
Palestinian Authority:
- Since the Oslo Accords of the 1990s, Bethlehem has been under the administration of the Palestinian Authority.
- The city continues to be a focal point for Palestinian culture and nationalism, while also attracting thousands of
Christian pilgrims annually, particularly during Christmas.
Cultural and Religious Significance
- Church of the Nativity:A UNESCO World Heritage Site, the church is a major pilgrimage destination for Christians
around the world.
- Religious Festivals: Bethlehem hosts numerous religious festivals and events, especially during Christmas, when
the city becomes a center of global Christian celebrations.
- Cultural Heritage: Bethlehem is known for its vibrant cultural life, including traditional crafts, music, and
dance.
Bethlehem's rich history and cultural heritage make it a unique and significant city, symbolizing both ancient
traditions and contemporary struggles. Its legacy as a birthplace of major religious figures and its ongoing role in the
Israeli-Palestinian conflict continue to shape its identity and significance on the global stage wikipedia
Ginin
Jenin is a city in the northern West Bank, Palestine, with a history that dates back thousands of years. It is known for
its agricultural richness and strategic location. Here is a detailed overview of Jenin's history and significance:
Ancient and Medieval History
Ancient Period:
- Early Settlement: Jenin, historically known as "Ein-Ganeem" or "Ginaea," has been inhabited since ancient times.
The area was known for its abundant springs and fertile lands.
- Canaanite and Israelite Periods:** The city has connections to ancient Canaanite and Israelite civilizations. It is
mentioned in Egyptian texts and in the Hebrew Bible.
Islamic and Crusader Periods:
- Early Islamic Period: With the spread of Islam in the 7th century, Jenin came under Muslim control and became
known as "Jenin." The city prospered under various Islamic dynasties.
- Crusader and Ayyubid Periods:Jenin was briefly occupied by Crusaders but was later recaptured by Saladin in the
12th century. It remained under Muslim control, flourishing as a market town.
Ottoman Period
British Mandate and Jordanian Rule
British Mandate (1917-1948):
- Modern Development:During the British Mandate, Jenin saw significant modernization, including infrastructure
development and urban expansion.
-Political Activity: The city was a center of political activity and resistance against British rule and Zionist
movements.
Israeli Occupation
Battle of Jenin
Six-Day War and Aftermath (1967-present):
- Occupation:In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Jenin was occupied by Israeli forces, leading to significant
political and social changes.
- Conflict and Resistance:Jenin has been a focal point of resistance against Israeli occupation, particularly
during the First and Second Intifadas. The city and its refugee camp have experienced intense military confrontations
and incursions.
Modern Jenin
Contemporary Era:
- Jenin Refugee Camp:Established in 1953 to accommodate Palestinian refugees from the 1948 war, the camp has become
a symbol of Palestinian resistance and suffering. It was the site of intense fighting during the Second Intifada in
2002, known as the Battle of Jenin.
- Cultural Revival: Despite challenges, Jenin has seen cultural and economic initiatives aimed at revitalization.
The Freedom Theatre, founded in 2006, is a notable cultural project promoting art and resistance.
Political Significance:
- Palestinian Authority: Since the Oslo Accords, Jenin has been under the administration of the Palestinian
Authority. It remains a significant center of Palestinian political and social activity.
Jenin's history is marked by its resilience and strategic importance, from ancient times through modern conflicts. Its
cultural heritage and ongoing struggles reflect the broader narrative of the Palestinian people wikipedia .
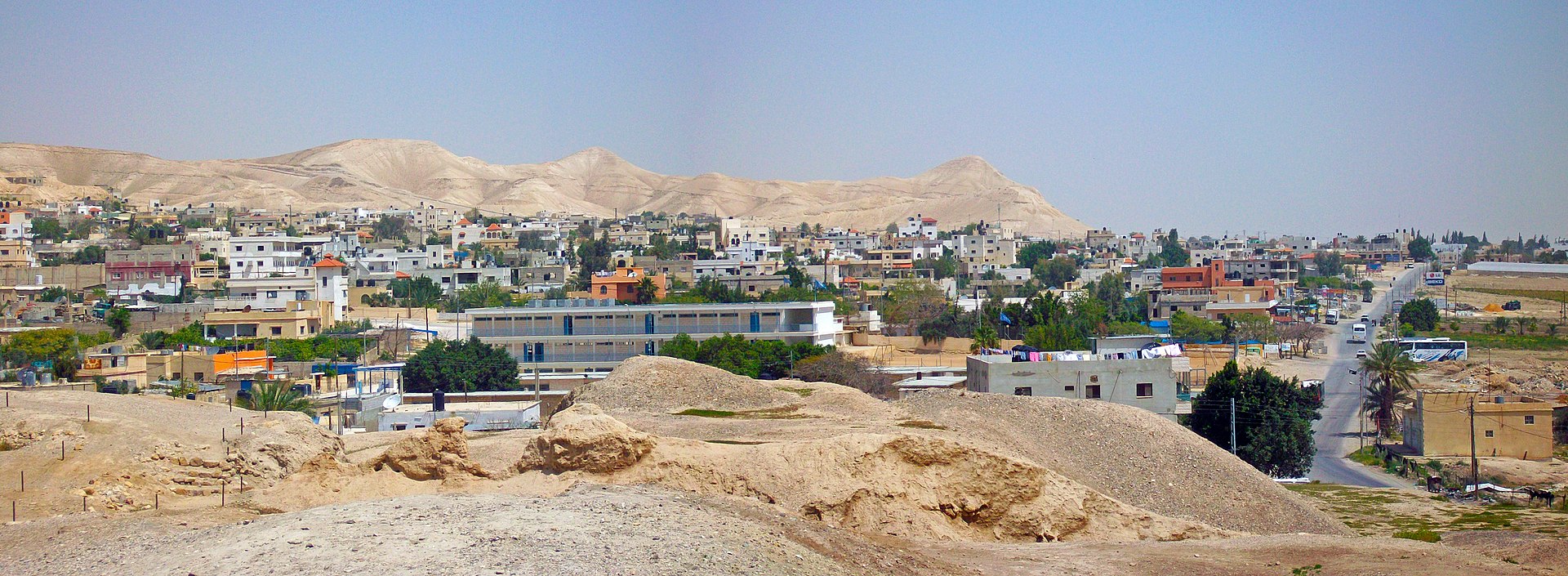
Jericho (Ariha)
Jericho, also known as Ariha in Arabic, is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Located in
the Jordan Valley of the West Bank, Palestine, it has a rich history that spans thousands of years. Here is an
overview of Jericho's history and significance:
Classical Antiquity
Byzantine Period:
- Christianity's Influence: Under Byzantine rule, Jericho continued to prosper. It became an important pilgrimage
site for Christians due to its biblical connections. Several churches and monasteries were built during this period.
Islamic and Crusader Periods
Early Islamic Period:
- Muslim Conquest: Following the Muslim conquest in the 7th century, Jericho remained an important agricultural hub.
The Umayyads built the Hisham's Palace, a significant archaeological site with notable mosaics and architecture.
Crusader and Ayyubid Periods:
- Crusader Control: Jericho briefly fell under Crusader control in the 12th century but was later recaptured by
Muslim forces under Saladin.
Ottoman Period and Modern Era
Ottoman Rule (1517-1917):
- Administrative Center: Jericho was part of the Ottoman Empire for several centuries. It served as an
administrative center and continued to be an important agricultural area.
British Mandate and Jordanian Rule:
- British Mandate (1917-1948): After World War I, Jericho came under British mandate control. It experienced
modernization and infrastructure development during this period.
- Jordanian Rule (1948-1967): Following the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Jericho was annexed by Jordan. The city saw
further development and population growth.
Israeli Occupation and Palestinian Authority
Israeli Occupation (1967-present):
- Six-Day War: In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Jericho was occupied by Israeli forces. The occupation brought
significant political and social changes to the city.
Palestinian Authority:
- Oslo Accords: After the Oslo Accords in the 1990s, Jericho was one of the first cities to come under the
administrative control of the Palestinian Authority. It remains a significant center of Palestinian governance and
culture.
Jericho's long and varied history, coupled with its agricultural richness and archaeological significance, make it a
unique and important city in the Palestinian territories and the broader Middle East. wikipedia.
Tulkarm (Tulkarem)
Tulkarm, also known as Tulkarem, is a city in the northwestern West Bank, Palestine. It has a rich history and plays
a significant role in the region's cultural and economic landscape. Here is an overview of Tulkarm's history and
significance:
Ancient and Medieval History
Ancient Period:
- Early Settlement: Tulkarm's history dates back to ancient times. The area was known for its strategic location
along trade routes and its fertile lands.
- Canaanite and Israelite Periods: Tulkarm has connections to ancient Canaanite and Israelite civilizations. The
city's location made it an important center for trade and agriculture.
Islamic and Crusader Periods:
- Early Islamic Period: With the spread of Islam in the 7th century, Tulkarm came under Muslim control. The city
prospered under various Islamic dynasties.
- Crusader and Ayyubid Periods: Tulkarm was briefly occupied by Crusaders but was later recaptured by Muslim forces.
It remained an important market town during these periods.
Ottoman Period
Ottoman Rule (1517-1917):
- Administrative Center: Under Ottoman rule, Tulkarm became an administrative center for the surrounding region. The
city saw significant development in infrastructure and trade.
- Agricultural Hub: Tulkarm was known for its agricultural productivity, particularly in the cultivation of olives,
citrus fruits, and grains.
British Mandate and Jordanian Rule
British Mandate (1917-1948):
- Modern Development: During the British Mandate, Tulkarm experienced modernization, including the development of
infrastructure and urban expansion.
- Political Activity: The city was a center of political activity and resistance against British rule and Zionist
movements.
Jordanian Rule (1948-1967):
- Annexation by Jordan: Following the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Tulkarm was annexed by Jordan. The city continued to
develop as an important urban center in the West Bank.
Israeli Occupation and Palestinian Authority
Israeli Occupation (1967-present):
- Six-Day War: In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Tulkarm was occupied by Israeli forces. The occupation brought
significant political and social changes to the city.
- Conflict and Resistance: Tulkarm has been a focal point of resistance against Israeli occupation, particularly
during the First and Second Intifadas. The city and its refugee camp have experienced intense military
confrontations and incursions.
Palestinian Authority:
- Oslo Accords: Since the Oslo Accords in the 1990s, Tulkarm has been under the administration of the Palestinian
Authority. It remains a significant center of Palestinian political and social activity.
Tulkarm's history is marked by its agricultural richness, strategic importance, and resilience. Its role in the
region's cultural and political landscape reflects the broader narrative of the Palestinian people. wikipedia.
Rafah (Rafiah)
Rafah, also known as Rafiah, is a city in the southern Gaza Strip, Palestine. It has a long and varied history and
is an important cultural and economic hub in the region. Here is an overview of Rafah's history and significance:
Ancient and Medieval History
Ancient Period:
- Early Settlement: Rafah has been inhabited since ancient times. The city's strategic location made it a key point
on trade routes between Egypt and the Levant.
- Egyptian and Canaanite Influence: Rafah was influenced by both Egyptian and Canaanite civilizations. It served as
an important border town and trade center.
Islamic and Crusader Periods:
- Early Islamic Period: With the spread of Islam in the 7th century, Rafah came under Muslim control and prospered
under various Islamic dynasties.
- Crusader and Ayyubid Periods: Rafah was briefly occupied by Crusaders but was later recaptured by Muslim forces,
remaining an important market town during these periods.
Ottoman Period
Ottoman Rule (1517-1917):
- Administrative Center: Under Ottoman rule, Rafah served as an important administrative and trade center for the
surrounding region. It saw development in infrastructure and agriculture.
- Agricultural Hub: Rafah was known for its agricultural productivity, particularly in the cultivation of crops like
wheat, barley, and fruits.
British Mandate and Egyptian Administration
British Mandate (1917-1948):
- Modern Development: During the British Mandate, Rafah experienced modernization, including infrastructure
development and urban expansion.
- Political Activity: The city was a center of political activity and resistance against British rule and Zionist
movements.
Egyptian Administration (1948-1967):
- After the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Rafah came under Egyptian administration. The city continued to develop and
played a significant role in the region.
Israeli Occupation and Palestinian Authority
Israeli Occupation (1967-present):
- Six-Day War: In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Rafah was occupied by Israeli forces. The occupation brought
significant political and social changes to the city.
- Conflict and Resistance: Rafah has been a focal point of resistance against Israeli occupation. The city and its
residents have experienced numerous military confrontations and incursions, especially during the First and Second
Intifadas.
Palestinian Authority:
- Oslo Accords: Since the Oslo Accords in the 1990s, Rafah has been under the administration of the Palestinian
Authority. It remains a significant center of Palestinian political and social activity.
Rafah's history is marked by its strategic importance, agricultural richness, and resilience in the face of
conflict. Its role in the region's cultural and political landscape reflects the broader narrative of the
Palestinian people. wikipedia.
Khan Yunis (Khan Younis)
Khan Yunis, also spelled Khan Younis, is a city in the southern Gaza Strip, Palestine. Known for its historical
significance and vibrant community, Khan Yunis plays an important role in the region's culture and economy. Here is
an overview of Khan Yunis's history and significance:
Ancient and Medieval History
Ancient Period:
- Early Settlement: The area around Khan Yunis has been inhabited since ancient times, benefiting from its strategic
location along trade routes.
- Canaanite and Egyptian Influence: The city's early history includes influence from Canaanite and Egyptian
civilizations, given its proximity to Egypt.
Medieval Period:
- Mamluk Period: Khan Yunis was officially founded in the 14th century by the Mamluk Sultan Barquq. The city was
named after the local leader Yunis al-Nurasi, who established a khan (caravanserai) to serve traders and pilgrims.
- Strategic Location: The khan and the adjacent fort made Khan Yunis an important center for trade and military
activities in the region.
Ottoman Period
Ottoman Rule (1517-1917):
- Administrative Center: Under Ottoman rule, Khan Yunis continued to thrive as an administrative and trade center.
The city benefited from its fertile agricultural land and strategic position.
- Agricultural Hub: The region around Khan Yunis was known for its agricultural productivity, particularly in the
cultivation of grains, fruits, and vegetables.
British Mandate and Egyptian Administration
British Mandate (1917-1948):
- Modern Development: During the British Mandate, Khan Yunis saw modernization, including the development of
infrastructure and expansion of urban areas.
- Political Activity: The city was a center of political activity and resistance against British rule and Zionist
movements.
Egyptian Administration (1948-1967):
- After the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Khan Yunis came under Egyptian administration. The city continued to develop and
played a significant role in the region.
Israeli Occupation and Palestinian Authority
Khan Yunis massacre
Israeli Occupation (1967-present):
- Six-Day War: In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Khan Yunis was occupied by Israeli forces. The occupation brought
significant political and social changes to the city.
- Conflict and Resistance: Khan Yunis has been a focal point of resistance against Israeli occupation, particularly
during the First and Second Intifadas. The city and its residents have experienced numerous military confrontations
and incursions.
Palestinian Authority:
- Oslo Accords: Since the Oslo Accords in the 1990s, Khan Yunis has been under the administration of the Palestinian
Authority. It remains a significant center of Palestinian political and social activity.
Khan Yunis's history is marked by its strategic importance, agricultural productivity, and resilience. Its role in
the region's cultural and political landscape reflects the broader narrative of the Palestinian people. wikipedia.